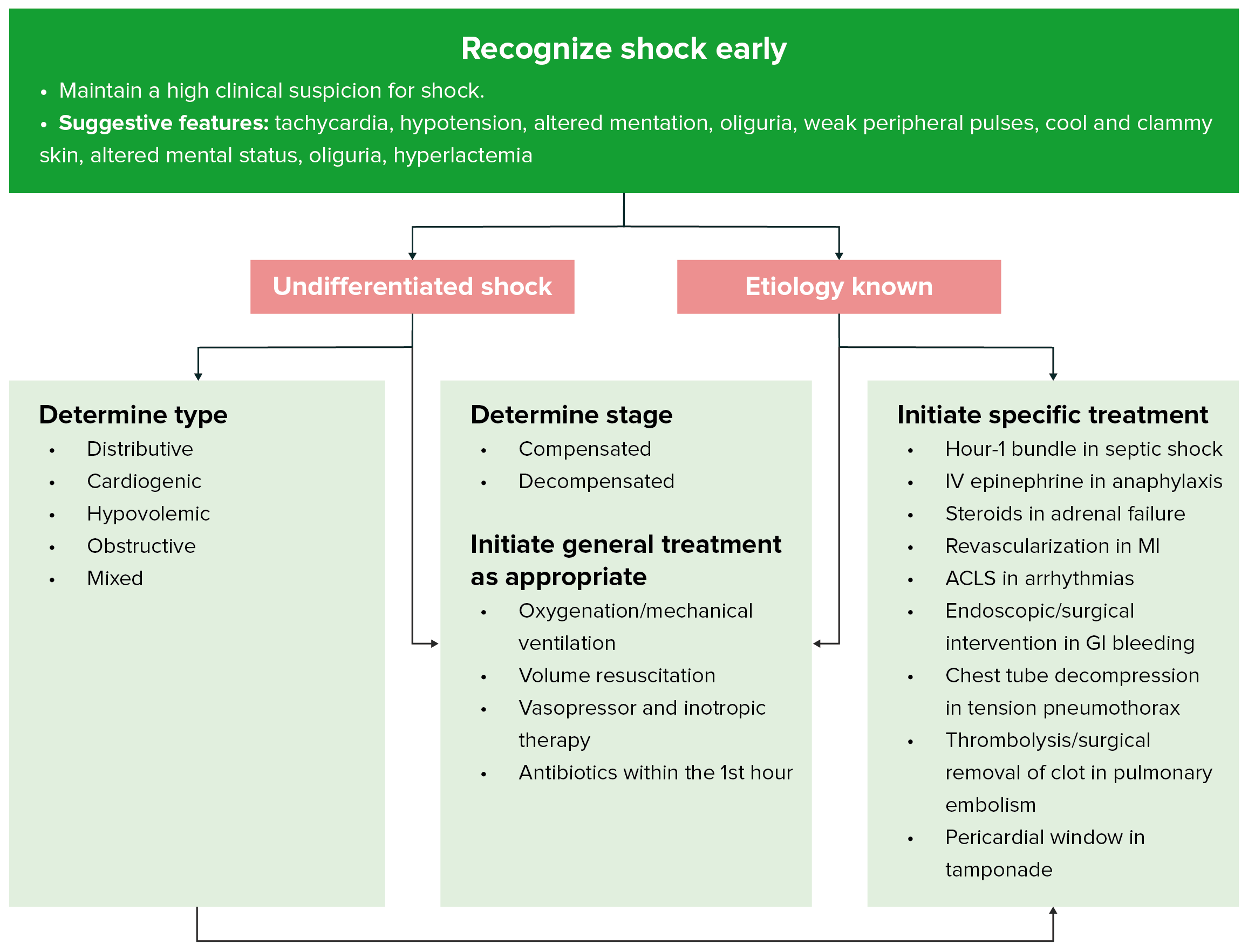
CI SVI and stroke work indices are usually decreased. The signs and symptoms of decompensated shock include.
Types Of Shock Concise Medical Knowledge
Neck vein distention rapid and severe hypotension tachycardia rapidly degrades into bradycardia and PEA.

. Vital signs are reassessed and are now Hr 134min BP 7040 mm Hg and SpO2 82. Symptoms may include shortness of breath weakness or altered mental status. What are the signs and symptoms of obstructive shock.
Distributive shock also known as vasodilatory shock is one of the four broad classifications of disorders that cause inadequate tissue perfusion. Increased work of breathing increased respiratory rate respiratory distress and diminished lung sounds on the affected side. Obstruction can occur at the level of the great vessels or the heart itself.
Because tissue perfusion is decreased the Mv o2 is low the arteriovenous oxygen content difference increased and serum lactate frequently elevated. Common symptoms include tachypnea tachycardia low to normal blood pressure decreased urine output and decreased level of consciousness. Hypovolemic shock is characterized by decreased intravascular volume and increased systemic venous assistance compensatory the mechanism to maintain perfusion in the early stages of shock.
Lung sounds are more present but are still diminished on the right side. Find an answer to your question True or false. Individuals with obstructive shock typically experience respiratory distress and may present with tachycardia hypotension tachypnea air hunger ie an extreme need to breathe and chest pain.
Early signs of obstructive shock always resemble distributive shock. Early signs of obstructive shock always resemble distributive shock. There are four respiratory core cases four core shock cases and four core cardiac cases.
Symptoms that are associated with neurological function include confusion loss of consciousness and inability to. These are all life-threatening. Obstructive shock is one of the four types of shock caused by a physical obstruction in the flow of blood.
However in veterinary medicine patients with cardiac disease more commonly present with signs of congestive heart failure and breathing difficulties rather than overt hypoperfusion and shock. Distributive shock also leads to leakage of fluid from capillaries into the surrounding tissues. The clinician shouldperform a thorough multisystem assessment in order to determine if signs of shock are present.
The signs and symptoms of decompensated shock are becoming more obvious and the increase in vasoconstriction results in hypoxia to the other organs of the body. If bleeding into the gastric system is the cause the patient might vomit blood or have bloody diarrhea. Patients may present with dyspnea compensatory tachycardia and poor perfusion.
What are the signs and symptoms of obstructive shock. The patient still has labored breathing. What follows is from that dvd.
In addition to an elevated heart rate all types of shock also typically present with rapid respiration. This form of shock is rare in veterinary patients but may be seen with pericardial effusion where the pressure in the pericardial sac reduces. Consider that there may be multiple etiologies of shock occurring simultaneously.
- As shock progresses the patient s neurologic status declines urine output decreases skin becomes cooler and mottled and peripheral pulses diminish. The symptoms that are related to the heart and its function are chest pain lightheadedness and a sudden increase in. Because of the decrease in oxygen to the brain the patient will become confused and disoriented.
Pale cool skin. Obstructive shock - Obstruction to blood flow. - The overall goals for a patient in shock include 1 evidence of adequate tissue.
In the later stages of shock due to progressive volume depletion cardiac output also decreases and manifest as hypotension. As the needle is inserted there is a rush of air coming from the hub of the needle. On auscultation a friction rub and distant heart sounds may be present.
As shock progresses peripheral pulses may not be palpable and a Doppler may be needed to detect the systolic blood pressure. Consider a broad differential diagnosis. Systemic vasodilation leads to decreased blood flow to the brain heart and kidneys causing damage to vital organs.
Here is the link to the 2006 PALS case studies. Alterations in mental status. Distributive and obstructive It is important to.
Shock may be obvious but often the. A characteristic sign of causative conditions like pneumothorax and tamponade may include dilated and engorged. Sweating diaphoresis As hypovolemic shock gets worse the patient becomes lethargic confused and eventually unconscious.
If external bleeding is the cause there will be blood. Because stroke volume is decreased the peripheral pulses are difficult to palpate and easily blocked. Patients with critical cardiac tamponade present with Becks triad of symptoms including hypotension quiet muffled heart sounds and raised jugular venous pressure 7 10 11.
However in veterinary medicine patients with cardiac disease more commonly present with signs of congestive heart failure and breathing difficulties rather than overt hypoperfusion and shock. Distributive shock is difficult to recognize because the signs and symptoms vary greatly depending on the etiology. Increased heart rate is the first sign of shock.
Obstructive shock - Obstruction to blood flow. Her SpO2 does not go above 82. Other hemodynamic parameters are dependent on the site of the obstruction.
This is because the fundamental problem in shock is lack of oxygen delivery to the bodys vital organs. The case studies were on the 2006 PALS dvd. Decreased level of consciousness.
False Martinez1343 Martinez1343 05162018 Biology High School answered True or false. This form of shock is rare in veterinary patients but may be seen with pericardial effusion where the. Causes include pulmonary embolism cardiac tamponade and tension pneumothorax.
Therefore the body tries to compensate for the lack of oxygen by breathing more rapidly.

Causes Of Shock In The Trauma Patient Download Scientific Diagram



0 Comments